Energy efficiency is a growing concern for many industries, and insulating glass plays a vital role in making our buildings and vehicles more energy-efficient. But have you ever wondered how this glass keeps its performance under tough conditions? The secret lies in the molecular sieve. Let’s dive into its incredible powers!
Insulating glass molecular sieve is a game-changer in glass technology. It helps absorb moisture and organic matter, ensuring smooth and transparent glass even in harsh weather. This extends the glass’s life and enhances performance.
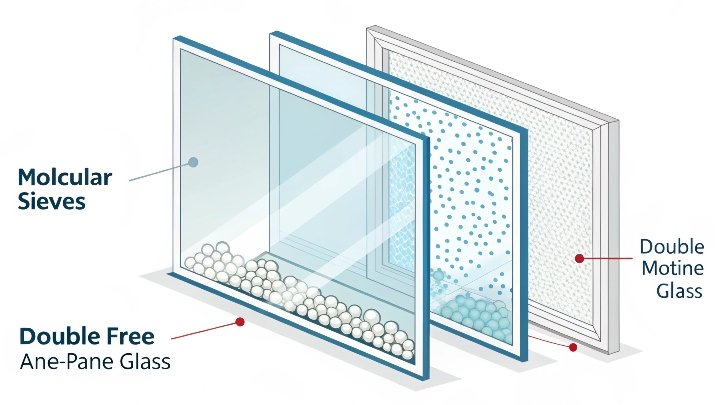
To understand why insulating glass molecular sieves are so important, we need to look at how they function. These tiny, spherical particles, made of crystalline aluminum silicate, absorb moisture and gases trapped inside the air layer between glass panes. Without them, temperature fluctuations can cause fogging, breakage, or distortion in the glass. The sieve helps maintain clarity, prevents fogging, and extends the lifespan of the glass, whether it’s used in homes, cars, or solar panels.
Enhancing Energy Efficiency: The Role of Molecular Sieves in Insulating Glass
What makes insulating glass more efficient in energy conservation? It all comes down to the molecular sieve’s ability to control moisture and gases trapped within the glass.
Molecular sieves enhance the energy efficiency of insulating glass by preventing condensation and maintaining the glass’s thermal insulation properties. By keeping the glass clear and free of moisture, they help reduce heat loss, which lowers energy consumption.
How Insulating Glass Molecular Sieves Contribute to Energy Efficiency
The most significant benefit of molecular sieves in insulating glass is their moisture-absorbing ability. When moisture is present between glass panes, it can result in condensation. This moisture creates thermal bridges that reduce the insulating properties of the glass. Over time, this leads to heat loss and increased energy consumption.
Molecular sieves are designed to capture moisture and gases that might otherwise condense. By doing so, they ensure the insulating glass retains its thermal efficiency. This is particularly important in buildings and vehicles, where maintaining stable internal temperatures is key to energy savings.
In homes and commercial buildings, insulating glass units (IGUs) are often used in windows and curtain walls. When these units are installed with molecular sieves, they not only prevent moisture buildup but also help reduce heating and cooling costs by improving the glass’s insulating properties.
This energy-saving technology has become a standard in modern construction. The impact on sustainability and energy conservation is significant, making insulating glass a preferred choice for environmentally conscious building projects.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Science Behind Molecular Sieve Drying
Ever wonder how molecular sieves actually work in drying applications? It’s not just about absorbing moisture — there’s more to the science behind this incredible material.
The drying process of molecular sieves goes beyond moisture removal. It involves adsorption, a process where water molecules stick to the surface of the sieve. This process makes the sieve extremely effective in preserving the integrity of the glass.
The Science of Adsorption: A Key Process
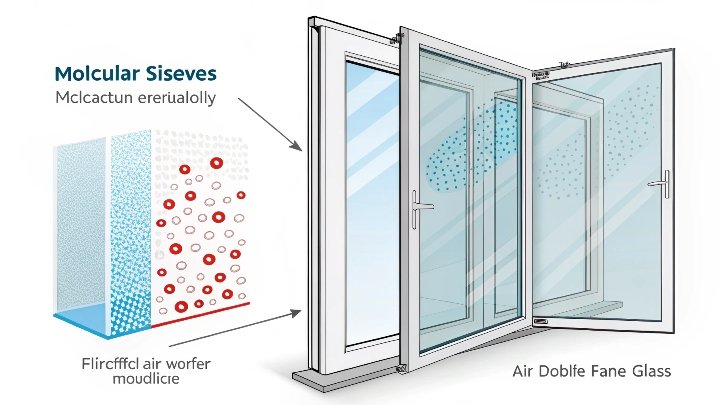
Molecular sieves are a type of adsorbent, meaning they capture molecules from the surrounding environment without actually absorbing them into their structure. The primary mechanism at play is adsorption, which occurs when molecules, such as water vapor, cling to the surface of the sieve. These sieves are designed with precisely sized pores that allow them to capture only specific molecules based on their size and shape.
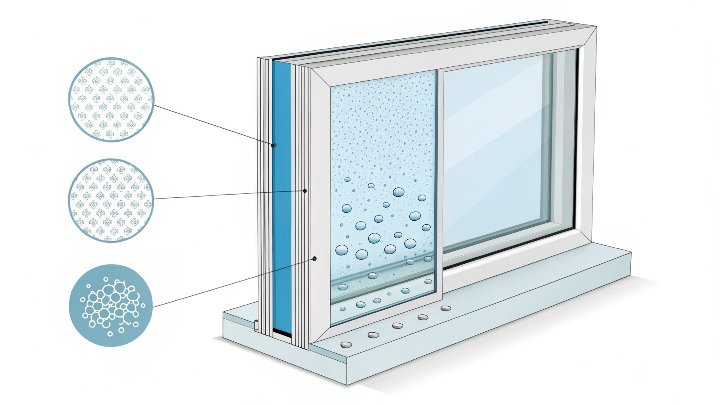
The pores in an insulating glass molecular sieve are typically around 3A in diameter, which is ideal for trapping water molecules. When air enters the interlayer between the panes of glass, moisture in the air is adsorbed by the sieve, preventing condensation from forming on the inner surfaces of the glass. This process also prevents the growth of mold or mildew, which could otherwise degrade the glass or the air quality inside a building or vehicle.
What’s fascinating is that molecular sieves can also capture other organic contaminants and gases. This versatility makes them incredibly valuable in a wide range of applications, from automotive glass to solar panels. By eliminating moisture and contaminants, the sieve ensures that the glass remains clear and functional, even under extreme weather conditions.
Why Molecular Sieves are Crucial for Glass Longevity
The impact of molecular sieves on the longevity of insulating glass cannot be overstated. In buildings, cars, and appliances, temperature fluctuations can cause significant internal and external pressure differences in glass. Over time, this pressure can lead to cracks, distortion, or even breakage.
Molecular sieves reduce this pressure difference by controlling the moisture levels inside the glass. This balance helps prevent the glass from expanding or contracting too much, thus extending its lifespan. For example, in architectural glass used for windows or curtain walls, molecular sieves play a critical role in maintaining the clarity and strength of the glass through all kinds of weather changes.
Improving Performance: The Key Benefits of Using Molecular Sieves in Glass Units
Is there a way to make insulating glass even better? The answer is yes — by using molecular sieves, we can significantly improve the performance of glass units.
By using molecular sieves, insulating glass units not only stay clear and free of moisture but also perform better under various conditions. These sieves help prevent distortion, improve the glass’s insulating properties, and ultimately reduce the risk of breakage.
Top Benefits of Molecular Sieves in Glass Units
-
Preventing Condensation: As we’ve discussed, moisture buildup is one of the biggest threats to insulating glass. Molecular sieves absorb moisture and prevent condensation, keeping the glass clear and functional. This is especially important in climates with high humidity or extreme temperature fluctuations.
-
Reducing Thermal Loss: The molecular sieve helps preserve the insulating properties of the glass by preventing the formation of thermal bridges. This reduces heat transfer and improves energy efficiency. Whether in homes, office buildings, or vehicles, molecular sieves enhance the glass’s ability to maintain stable internal temperatures, leading to lower energy bills.
-
Increasing Durability: The ability of molecular sieves to balance internal pressure differences reduces the likelihood of glass distortion or breakage. This makes them an essential component for both automotive glass and architectural glass, where durability is key.
-
Enhancing Aesthetics: By keeping the glass clear and free of moisture, molecular sieves also help maintain the aesthetic appeal of insulating glass. Whether in windows, solar panels, or refrigerated compartments, the clarity of the glass improves the overall look and functionality of the product.
Conclusion
Incorporating molecular sieves into insulating glass not only boosts energy efficiency but also enhances the glass’s longevity, performance, and appearance. The benefits are clear and essential for a wide range of applications, from homes and cars to solar panels and refrigerated compartments.